As Pakistan continues to face rapid urbanization and population growth, the demand for affordable housing has reached critical levels. The growing number of people moving to cities has strained existing housing infrastructure, leading to overcrowding, informal settlements, and a lack of basic services in many urban areas. In response to this challenge, smart cities are gaining momentum as a potential solution. Smart cities aim to leverage technology and data-driven systems to create more sustainable, efficient, and inclusive urban environments. One notable example in Pakistan is Capital Smart City Islamabad, a project that integrates advanced technologies with sustainable urban planning to address the country’s housing needs, especially in the affordable housing sector.
Overview of Capital Smart City
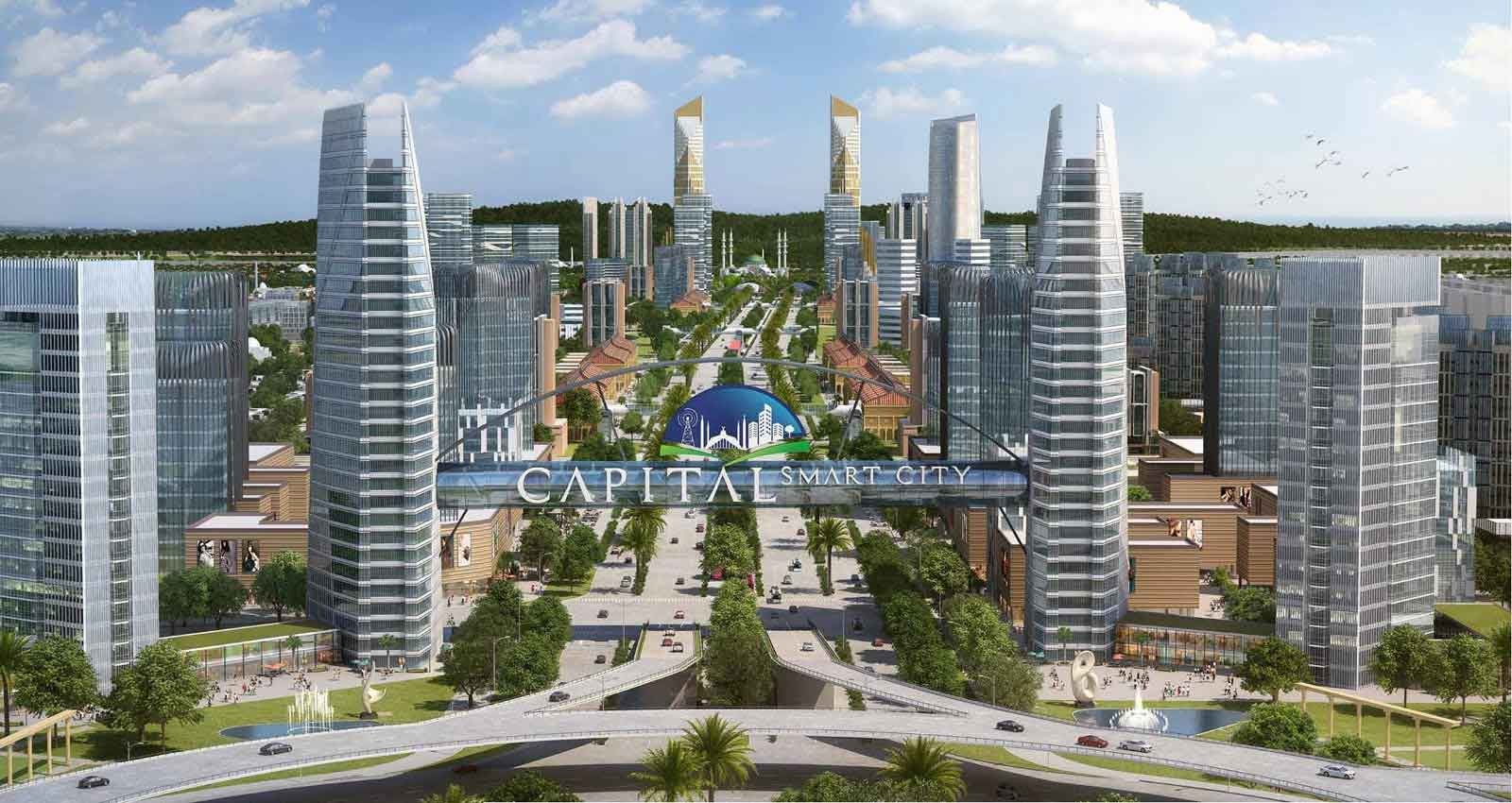
Capital Smart City Islamabad is one of Pakistan’s first smart city projects and is designed to meet the growing housing demands in the twin cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi. It is strategically located near the New Islamabad International Airport, along the M-2 Motorway, giving it a prime position in terms of connectivity and accessibility. The goal of the project is to create a self-sustaining, technology-driven urban environment that provides modern living standards for its residents. The city incorporates state-of-the-art technology in areas such as resource management, transportation, public safety, and housing, all aimed at improving the quality of life while ensuring sustainability and affordability.
The project has been developed with a vision to create a smart city that not only offers high-quality living but also caters to a wide range of socio-economic groups, including low- and middle-income families. The introduction of affordable housing within this framework is a key focus, as it aligns with the broader goal of creating inclusive urban environments that do not exclude the less affluent members of society.
Key Features Promoting Affordable Housing
- Smart Infrastructure and Resource Management
One of the key features of Capital Smart City is its emphasis on smart infrastructure. The city makes extensive use of data analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to monitor and optimize the use of resources such as water, electricity, and waste management. This smart infrastructure helps reduce operational costs by managing resources more efficiently and minimizing waste. For housing developments, this can translate into lower utility costs and maintenance expenses, which in turn can help keep housing prices and rents more affordable for residents. By passing on these savings, Capital Smart City aims to make modern living more accessible to a broader population. - Sustainable Practices and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability is a key pillar of the development strategy for Capital Smart City. The city is designed to incorporate energy-efficient buildings and sustainable urban practices that help reduce the environmental impact of urbanization. Housing units are equipped with smart technologies that monitor energy consumption, promote the use of renewable energy sources such as solar power, and ensure proper insulation to minimize energy waste. These features not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also help lower energy bills, making homes more affordable for low- and middle-income families. By integrating sustainability into the housing sector, Capital Smart City aims to create homes that are both cost-effective and eco-friendly. - Community Engagement and Inclusivity
A key component of Capital Smart City’s development philosophy is community engagement. The project seeks to involve local communities in the planning and decision-making processes to ensure that the needs and preferences of residents are reflected in the design and implementation of the city’s infrastructure. This approach helps promote inclusivity by preventing the displacement of long-standing communities due to gentrification or rising property prices. By focusing on the needs of both current and future residents, the city aims to create a living environment that is inclusive, welcoming, and beneficial for all socio-economic groups. The involvement of local communities also fosters a sense of ownership and belonging, which is crucial for the long-term success of any urban development project.
Challenges and Considerations
While the development of Capital Smart City Islamabad presents numerous opportunities to address affordable housing, it also faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the success and sustainability of the project.
- High Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary challenges of implementing smart city technologies is the high initial investment required for infrastructure and technology deployment. Smart cities rely on the integration of advanced systems such as IoT networks, data centers, smart grids, and automated services, which can be costly to install and maintain. For developers, these high upfront costs may serve as a deterrent when considering affordable housing projects, as they may prioritize more profitable, high-end developments to recover their investment. This challenge highlights the need for policy interventions and government support to incentivize developers to focus on affordable housing within smart cities. - Digital Divide and Technological Inclusivity
Another critical challenge facing the development of smart cities, particularly in Pakistan, is the digital divide. While smart city technologies can improve the quality of life for residents, not all socio-economic groups have equal access to the necessary digital tools and services. Low-income families and marginalized communities may lack the financial resources or digital literacy to fully benefit from the smart features of the city. This creates the risk of exclusion, where only wealthier residents can take advantage of the technological advancements. To address this issue, it is essential to implement programs that provide access to affordable technology and digital education, ensuring that all residents can participate in and benefit from the smart city environment. - Policy Alignment and Public-Private Partnerships
Effective collaboration between government entities and private developers is crucial for the success of smart city projects like Capital Smart City. Aligning policies that promote smart city development with affordable housing initiatives requires coordination between multiple stakeholders, including municipal authorities, developers, and financial institutions. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can play a key role in overcoming some of the financial and logistical barriers associated with smart city development. Through these partnerships, governments can provide incentives, such as tax breaks or subsidies, to encourage private developers to invest in affordable housing projects while ensuring that these projects align with broader smart city goals.
Global Comparisons: Lessons from Other Smart Cities
Pakistan can also look to the experiences of other countries that have successfully integrated affordable housing within smart city frameworks. For example:
- Singapore: In Singapore, the Punggol Digital District is a model for integrating affordable public housing with smart city technologies. The district uses IoT devices to manage resources like water and electricity efficiently, while ensuring that housing remains affordable for residents. The emphasis on both technology and affordability makes Singapore a global leader in smart urban development.
- India: India’s Dholera Smart City is another example of how developing countries can balance smart city infrastructure with affordable housing. The city is designed with smart technologies like smart grids and digital governance systems, while also prioritizing affordable housing solutions to accommodate its growing population.
Conclusion
The development of Capital Smart City Islamabad marks a significant step toward integrating smart technologies with affordable housing in Pakistan. By focusing on sustainability, community engagement, and efficient resource management, the project has the potential to address the country’s urgent need for affordable housing while setting a new standard for future urban developments. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, the digital divide, and the need for policy alignment must be carefully managed to ensure that the project achieves its goals of inclusivity and affordability.
In the long run, the success of Capital Smart City will depend on how well it can balance innovation with inclusivity. As smart city projects continue to develop in Pakistan and other parts of the world, it is crucial to ensure that all segments of society, including low- and middle-income families, can share in the benefits of technological advancements and improved urban living conditions.